info retrieval view markdown
Some notes on information retrieval, based on UVA"s Info Retrieval course.
introduction
- building blocks of search engines
- search (user initiates)
- reccomendations - proactive search engine (program initiates e.g. pandora, netflix)
- information retrieval - activity of obtaining info relevant to an information need from a collection of resources
- information overload - too much information to process
- memex - device which stores records so it can be consulted with exceeding speed and flexibility (search engine)
- IR pieces
- Indexed corpus (static)
- crawler and indexer - gathers the info constantly, takes the whole internet as input and outputs some representation of the document
- web crawler - automatic program that systematically browses web
- document analyzer - knows which section has what -takes in the metadata and outputs the index (condensed), manage content to provide efficient access of web documents
- crawler and indexer - gathers the info constantly, takes the whole internet as input and outputs some representation of the document
- User
- query parser - parses the search terms into managed system representation
- Ranking
- ranking model -takes in the query representation and the indices, sorts according to relevance, outputs the results
- also need nice display
- query logs - record user’s search history
- user modeling - assess user’s satisfaction
- Indexed corpus (static)
- steps
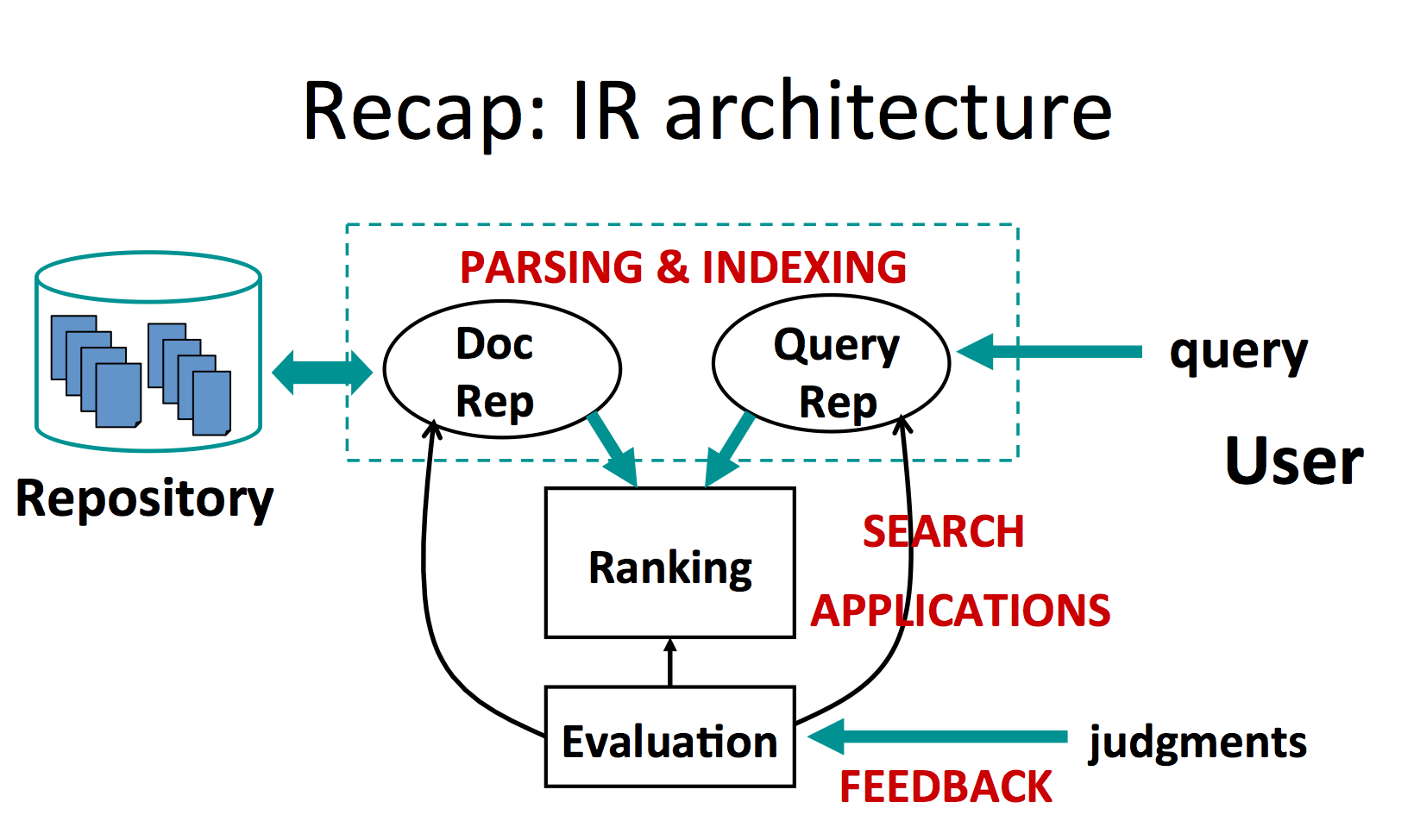
- repository -> document representation
- query -> query representation
- ranking is performed between the 2 representations and given to the user
- evaluation - by users
- information retrieval:
- reccomendation
- question answering
- text mining
- online advertisement
related fields
they are all getting closer, database approximate search and information extraction converts unstructed data to structured:
| database systems | information retrieval |
|---|---|
| structured data | unstructured data |
| semantics are well-defined | semantics are subjective |
| structured query languages (ex. SQL) | simple keyword queries |
| exact retrieval | relevance-drive retrieval |
| emphasis on efficiency | emphasis on effectiveness |
- natural language processing - currently the bottleneck
- deep understainding of language
- cognitive approaches vs. statistical
- small scale problems vs. large
- developing areas
- currently mobile search is big - needs to use less data, everything needs to be more summarized
- interactive retrieval - like a human being, should collaborate
- core concepts
- information need - desire to locate and obtain info to satisfy a need
- query - a designed representation of user’s need
- document - representation of info that could satisfy need
- relevance - relatedness between documents and need, this is vague
- multiple perspectives: topical, semantic, temporal, spatial (ex. gas stations shouldn’t be behind you)
- Yahoo used to have system where you browsed based on structure (browsing), but didn’t have queries (querying)
- better when user doesn’t know keywords, just wants to explore
- push mode - systems push relevant info to users without a query
- pull mode - users pull out info using keywords